(1) Convex lenses
(2) Concave lenses
Differences between convex and concave lenses
(a)convex lenses
~Convex lenses are also known as converging lenses or positive lenses.~Convex lenses are thicker in the centre than at the edge.
~Cross-sectional views of common types of convex lenses:
~Convex lenses refract incident rays of light,which are parallel to the principal axis,so that they converge to a point on the principal axis.This point is called the real principal focus.
(b)concave lenses
~Concave lenses are also known as diverging lenses or negative lenses.
~Concave lenses are thinner in the centre than at the edge.
~Cross-sectional views of common types of concave lenses:
~Concave lenses refract incident rays of light , which are parallel to the principle axis ,so that they appear
to diverge from a point located on the incident side of the principal axis. This point is called the virtual
principal focus.
Common terminology
(a) convex lens
(b) concave lens
Power of a lens
*The power of a lens is a measure of the ability of the lens to converge or diverge rays of light.
*The formula for the power of a lens is:
Power(D)=1/Focal length(m)
=1/f
*unit of the power of lens is dioptres or D.
*A convex lenses has a positive focal length and power.
*A concave lenses has a negative focal length and power.
Ray Diagrams
*to determine the position and characteristics of images formed by lenses for any position of the object.
*can be completed using any two out of the three rays of light.
Images Formed by Convex Lenses
(a) Distant object , u = infinity
Image distance: v = f
*Real
*Inverted
*Diminished
*On the opposite side of the object
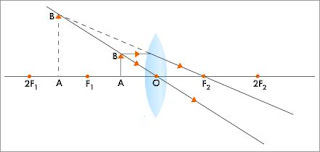
(b)Object distance is more than 2f, u>2f
Image distance: f<v<2f
*Real
*Inverted
*Diminished
*On the opposite side of the object
(c)Object distance is equal to 2f ,u=2f
Image distance : v = 2f
*Real
*Inverted
*Same size as object
*On the opposite side of the object
(d)Object distance is between f and 2f , ,f<u<2f
Image distance:v>2f
*Real
*Inverted
*Magnified
*On the opposite side of the object
(e)Object distance is equal to f, u=f
Image is at infinity
*virtual
*Upright
*Magnified
*On the same side as the object
(f)Object distance is less than f ,u<f
Object distance:v>u
*virtual
*upright
*magnified
*On the same side as the object
Images formed by Concave Lenses
*do not depend on the position of the object with respect to the lens
*an image formed by a concave lens is a always
(a)virtual
(b)upright
(c)smaller than the object
(d)located between the lens and the object
(e)the image distance is less than the focal length
Linear Magnification
*the ratio of the size of the image to the size of the object.
Linear magnification, m=size of image/size of object
The Use of Lenses in Optical Devices
Differences between microscope and telescope
(a) Microscope
*A compound microscope is an optical instrument used to view very small or fine objects.
*A compound microscope consists of two convex lenses of high power.
(a) The lens nearer the object is called the objective lens , with focal length,f。
(b) The lens nearer the eye is called the eyepiece , with focal length,fe'
*The objective les has a higher power as it has a shorter focal length compared to the eyepiece.
(b)Astronomical Telescope
*an astronomical telescope is an optical instrument that is used to view object at a great distance , such as
planet and stars.
*an astronomical telescope consists of two convex lenses. The objective lens whose power is low has along focal length,fo.The eyepiece whose power is high has a short focal length fe.
*the distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece is (fo+fe).












u are so hardworking !
ReplyDeleteDo this blog+_+
convex&concave lens are useful!!
ReplyDeleteem...very detail & understand, beautiful pic
ReplyDelete